When Robert Kaplan and Thomas Johnson wrote
about the fall of management accounting systems and pleaded for new
perspectives and approaches to strategic process control they wrote a most
relevant statement that still stands today. But as organisations are
implementing performance measurement systems as applications of their business
intelligence infrastructure, news risks of losing the most relevant part of strategic
management arise. There is a clear need for a new, extended approach to the
balanced scorecard (BSC). If you wonder what this may be, then read more.
In this
article I describe the generic strategy process, compare this with the
performance management process, how it is implemented in some organisations and
analyze the aspects of this process related to the organization’s leadership
style and thus the consequences for the balanced scorecard’s effectiveness.
The Strategy Process:
Formation and Formulation
Every
organisation has its own way of forming and formulating a strategy. It is in
the organizational DNA: the way strategic objectives are grounded on a clear
problem statement, SWOT analysis, competitive analysis, etc… and evaluated,
proper to that same DNA.
 |
Fig 1. The Strategy Process The strategic objectives entail the position of
the company for mid- and short term, wanted behavior from clients, associates
and partners. These objectives are then dissected, evaluated, scored and
appreciated according to the organization’s values and beliefs, the
organizational culture and past experience.
The last phase is the decision
phase where the objectives are translated into concrete actions and measurable
products and outcomes of these actions.
In the definition process, the strategic problems and opportunities are described and expressed in statements like: “We are not well positioned in the high end market”. Input for this process step is SWOT analysis, as well as analysis of the competition and the customer base. In the dissection process, expressions like “We are not well positioned…” are set in context and translated into critical success factors, e.g. “In order to improve our position in the high end market we need to upgrade our image, educate the sales force, identify more high end customers.” The eva luation process is mainly concerned with prioritizing the dissected elements and looking for causal relationships between these elements to prepare a cohesive and consistent strategic plan which can be communicated to all parties concerned. Finally in the decision process, the prioritized and feasible targets and ways to achieve these targets with global action plans are chosen. Some targets are based on decisions with tangible and measurable results and others are based on long term decisions with immaterial and almost immeasurable outcomes. The following decision points are ranked from very concrete and “hard” targets to more “soft” and less quantifiable decisions:
In the strategy formulation process steps, communication exercises will adjust these elements to match them with the various target groups: associates, clients, suppliers, shareholders, government officials, press, etc…
The Degrees of
Collaboration in the Strategy Process
If we
imagine a continuum in leadership styles, ranging from autocratic to democratic
leadership, the four strategy formation process steps will be subject to shared
inputs, transformation and outputs on a scale of zero to hundred percent.
In an autocratic leadership all four process
steps are in the hands of the leader. Only the leader decides what is important
in the environmental scan, what the objectives are, how the actions are prioritized. Some autocratic leaders have
problems formulating the strategic plan as they still hold up the adage
“knowledge is power”. What they gain on control may get lost in the execution
phase when their subordinates try to interpret their ambiguous communication.
Long time
ago, I studied the biographies of dictators (which names I won’t mention
because they deserve to be forgotten) and it struck me that often they
communicated very vaguely about their strategic vision, priorities, objectives
and the way to accomplish these objectives. Zealous and ambitious subordinates
would then translate these cryptic messages into complete (and often horrific)
action plans which would then be meticulously and ruthlessly executed. After
which the dictator either rewarded the zealot or had him sent in exile because
he became too popular or was a liability for the regime to the outside world. Nevertheless, autocratic leaders can be highly
successful in process industries, retail, service organisations and this
leadership style emerges everywhere there is a crisis and fast response times
are more important than a well pondered decision making process, balancing all
market factors, interests and wishes in the organisation.
In the democratic
leadership all four process steps may be in the hands of the entire team.
Lengthy discussion and negotiation may require a lot of resources but the
upside is that everyone in the organisation is on the same page and the
execution phase has less need for control and clear instructions as the
organisation members act in a more autonomous way, responding faster to changes
on the terrain. Organisations of professionals prefer democratic leadership as
knowledge and competence are far more important than rank and power and the
status that go with it.
Finally in mixed forms, the definition process may
be initiated by the strategic apex, shared with the ranks and business analysts
may be called in to dissect the statements into
manageable chunks.
The
evaluation and the decision process, depending on the level of democratic
leadership, may be done by the leader, a management team or a management team
extended with staff members and analysts.
Today, as
organisations become flatter and more democratic leadership styles are proper
to new industries, there is a need for faster feedback loops to combine the
advantages of autocratic leadership with the responsiveness of democratic
organisations.
The Performance Management
Process
The
strategy process, seen from a performance management perspective, is a
machine-like approach to define, monitor and manage the actions as defined in
the strategic plan.
Let’s see
how the strategy process is broken down into the performance management
process. The performance management process breaks down the strategy formation process
into smaller chunks to decompose the formation (definition, dissection,
evaluation and decision) into nine steps.
This is a
top down exercise:
·
Analyze
the situation (SWOT, competition,…) (Definition Process)
·
Determine
the objectives after the analysis (Definition Process)
·
Define
the critical success factors (CSF) (Definition & Dissection Process)
·
Derive
the critical performance indicators (CPI) from these CSFs (Definition &
Dissection Process)
·
Mapping
the CPIs on the organizational units down to the individual associate
(Dissection & Evaluation Phase)
·
Adapting
the HRM policies to these mappings (if trade unions allow, of course)
(Evaluation Process)
·
monitor,
manage and readjust the CPIs (Execution process)
·
monitor,
manage and readjust the CSFs (Execution process)
·
Adapt the
objectives to the new SWOT results (Execution process)
Remark how
implicit the decision process is embedded in the dissection and evaluation
process steps of the performance management approach.
Strategy automation?
In the past
ten years I have worked on IT-support for balanced scorecards (BSC) in a
university, a bank, an insurance company and a manufacturing company. In all of
these cases, a poignant conclusion was unavoidable: “If all you use is a
hammer, everything starts looking like a nail”. The ICT tool became a
substitute for the strategy process and forced a freeze on the organisation.
Let me explain this.
The BSC was
used as an instrument to implement a top down strategic governance of the
organisation. The strategy decomposition as described above is then modeled in
the ICT tool creating links and correlations between the various CSFs and CPIs.
Identifying these cause and effect chains is not a trivial matter. If sales go
south, all sorts of explanations may present themselves to the organisation.
E.g.: Are lower sales due to:
·
… lower
consumer confidence?
·
… a
competitive move?
·
… a
government announcement?
·
… simple
seasonality or a gradual shift in seasonality?
·
… the
weather?
·
… all of
the above?
Or can the
sales slump be explained by a factor we can influence like the number of sales
training hours received by the sales reps? But then the question arises if
there is a correlation between the amount and quality of the training received
and employee satisfaction? Or is it the other way around: because our employees are not very satisfied
with their job, they respond poorly to the training received[i]?
But that is
not all. As we all know, strategic management is about adapting to the
environment. If the ICT tool does not capture the environmental change either bottom up or
top down, then what? There is also another side of the coin: if the strategic
decomposition leads to individual targets, personal development plans and other
HRM tools how does this affect the flexibility of the organisation to adapt to
change?
People act
accordingly to the incentives from management: either they integrate the CPIs
in their work planning and their approach to the job or they look for ways to
beat the system. I remember sales people holding back order forms for a yearly
publication to “smoothen” the CPI measures of bookings per month since
management did not take seasonality into account when the performance indicator
was defined.
Strategy Dialectics
Are the Way Forward
It is clear
that the latter is unwanted behavior but those who conform with the system
should be rewarded, shouldn’t they?
The answer
is an ambiguous “Yes and No”. “Yes” if their response, steered and governed by
the performance indicator, is in sync with customer demand. And “No” if this is
not the case. Needless to add that any strategy which is not sanctioned by your
customers is not worth the paper it is written on.
But how are
the designer, the monitor and the manager of the balanced scorecard to know
this? Henry Mintzberg (1994)[ii]
makes the distinction between intended and emergent strategies and the way I
see it and experienced it, the balanced scorecard is an almost perfect tool for
managing intended strategies. It uses a negative feedback loop, just like a
thermostat. And just like a thermostat it sometimes oversees the efforts needed
to keep everybody in line with the intended strategy. So people who don’t meet
their targets are stimulated to do so or they are made redundant if they are
not likely to comply with the desired behavior. But as John Lennon so rightly
said “life is what happens while you are making other plans”. Management may
have misinterpreted the signals from the environment or changes in the market may
be unnoticed by management. In that case,
emergent strategies may provide the answers to these situations as there
is some form of “wisdom of the crowds” in the collective response from front
office workers and anyone else who is in contact with customers, competitors,
prospects, suppliers, researchers and government officials, to name a few. To
capture these emergent strategies, the system needs to provide positive
feedback loops to reinforce unplanned but successful behavior, even when it is
non compliant with the intended strategy. In other words, if top management
makes a mistake, it will get noticed in three to five years but if the front
office worker makes a mistake, the organisation has an acute problem.
This calls
for a special form of management, allowing dissidence in the ranks and
considering experimenters and contrarians as assets instead of a liability. “Is
this May 1968 all over again, when it was forbidden to forbid?”, I hear you
say. No, thanks.
But imagine
an organisation form where the exchange between the hierarchy and the ranks is
formalized, open, unbiased and where everyone’s fact findings and opinions are
accessible to everyone for discussion, refining and leading to decisions and
actions.
Imagine a
special form of knowledge management which goes further than a glorified chat
room and text mining.
Imagine a
system supporting both bottom up and top down strategy processes, using the
collective wisdom of the entire organisation. Technology may be able to design
and build such a system but if management is not prepared to adapt its ways of
developing, forming and formulating strategies then the developers needn’t
bother.
Knowledge Management
and Performance Measurement Systems in Modern Organisations
Remember
the initial point I was making: intended strategy is only a partial explanation
of the realized strategy because emergent or grassroots strategies contribute
to-or reduce- the results of the intended strategy. Since no entrepreneur or
manager likes to be only partially in control, we need a new approach to the
balanced scorecard implementation. Maybe that won’t be enough, maybe we need to
extend the scorecard’s toolset.
What if the exchange process were more
important than the results of it?
What if the
true outcome of the dialectic strategy process were -other than a plan with
measurable results:
·
enhanced
motivation because people see the context, the bigger picture and have
contributed to it,
·
a shared
vision and sense of direction that enhances group cohesion,
·
a higher
level of entropy, turning each individual into autonomous decision making
entities without the usual chaotic side effects,
·
increased
responsiveness to changing conditions or unexpected phenomena in the market?
What if the strategy process became a strategy
dialogue?
What if the
system could capture the dialogues between the workers and:
•
middle- and top management,
•
the customers,
•
the suppliers,
•
consultants,
•
academics,
•
opinion leaders,
•
government officials,
•
the data warehouse,
•
the external information sources?
What if this dialogue were supported by a tool
requiring almost no extra effort from the organisation?
Let’s
examine the actions people perform in an office which are –often without
knowing- valuable strategic information bits and are already captured partly or
wholly by the existing systems.
Searches on
the Intra- and Internet,
Consulting
information providers ranging from Wikipedia to academic and government
sources,
Sending and
receiving e-mails,
Creating
and reading documents like meeting notes, documentation, process descriptions,
…
Handling
customer complaints
Dunning
customers,
Online and
offline meetings, chats,
Analysis
and decision making,
etc…
All these
activities leave traces in some or another information system. What if you
could combine the most relevant words and constructs into input for your
strategic plan, supported by a balanced scorecard approach but avoiding a rigid
approach to the strategic process management? Let me have a go at specifying
such a system and check if the technology is already available.
Performance
Measurement Systems 2.0., a Functional Specification
The short
description of this system is: ”A Collaborative Strategy Process Manager” The
architectural view is visualized in the schema below.
Fig. 2. The Core Architecture of a Collaborative Strategy Process Manager The architectural picture consists of three interconnected pillars: strategy, individual development and knowledge support. For simplicity reasons we leave aspects like servers, APIs and user interfaces out of the schema. Only the relevant functional blocks are listed. Remark that the planning and execution of the strategy is not in scope. Tools like ERP and CRM can provide the necessary support for that part.
The Organizational Strategy Management Process: this is basically the support for
the balanced scorecard with a link to the personal development plans of the
people needed to execute the strategy. We refer to vendors like QPR, SAS, and
others to discover the features of a balanced scorecard software. But the link
to personal development plans (PDP) needs to be established. Imagine this PDP
as a database with relevant and “nice to have” competence development plans
which are maintained during appraisal and evaluation interviews. If the HRM application
can make the link with salary scales, a proper analysis can match the desired
competences with the future wage cost trend.
The Individual Development Support: this is a personal balanced
scorecard where the interconnections between interests, competences, knowledge
and the track record inside and outside the organisation are managed. Imagine a
kind of personal LinkedIn with extra depth in the competence area. Instead of
generic labels like “marketing” one would find hierarchies like “Marketing >
Market Research>Qualitative Market Research>Focus Groups>Brand
Experience”
The Knowledge Support System: this pillar is not readily
available of the shelve, but some components are.
The first
block Search Engine Logs and Ratings bundles the information search
behavior, the rating of the results but also the ratings of colleagues search
results, and all other communication and processed information. It also
includes ratings for decisions to be made by a group or an individual be it
multicriteria analysis, simple voting, rule based decision making or more
complex algorithms like ELECTRE. Bundling the information search and decision
behavior can yield interesting results for the knowledge management team
answering questions like “What information did he/she (or didn’t!) look for
before making a decision?”
The Object
Database is the engine behind
the object aware user interface, suggesting hyperlinks whenever users integrate
(potential) knowledge objects like information sources, notions, definitions,
persons, etc… in their communication. This forces users to be clear about what
they communicate and to what ontologies[i]
their concepts relate to. These objects, ready for the object aware user
interface are structured and edited by a knowledge manager or by the group,
depending on the configuration which supports both autocratic and democratic
environments. But the object database will also act as a repository for
unstructured data which can then be presented to the group or the knowledge manager
by “emerging publishers”.
The Object
Database also disposes of easy configurable agents which respond to events or
trigger events themselves, e.g. “Present the weekly list of most used
ontologies”.
The Knowledge
Modeling System is where ontologies, learning blocks and documentation
blocks are created and managed. These learning blocks and documentation blocks
are complete sentences or groups of sentences whether or not combined with
illustrations to create the basic material for documentation like ISO process
descriptions and procedures, help files and learning material for distance
learning or learning on the job.
Finally, the E-Learning System is where the
previous material is used in learning paths, documentation maps and presented
in a presentation layer which can be simple text and image, sound and/or video.
The material can be used on purpose or pop up spontaneously whenever users struggle
with knowledge gaps.
The three connections: the first connection is between the
organizational strategy management and individual development tools. With this
link, important questions can be answered and reality checks become
possible. A sample of these questions
and checks:
•
“Do
we have the competences in house to deliver the desired actions?”
•
“How
big is the knowledge gap we need to close”
•
“Where
are biggest obstacles for change management?“
•
“What
unused competences suggest opportunities for new strategic directions?”
The second
connection, between individual development and knowledge support tools makes
knowledge management more manageable by delivering information to questions
like:
The third
connection, between the strategy management support and the knowledge support
challenges assumptions and probes for answers to questions like:
· “Have we made the CSFs and KPIs sufficiently operational for the workforce to understand, adopt and apply them?” · “What level of comprehension of the strategy matches with a certain level of compliance to the proposed KPIs?”
· “What new information can influence adjustments to the initial strategy?“What new information can influence
adjustments to the initial strategy?”
If the
“What” and the “Why” are implemented properly, the “Where” and the “How” will
become easier to manage in an adaptive way because management control 2.0. will
increase self control with individuals and groups but leave enough room for new
initiatives to respond better to consumer demand.
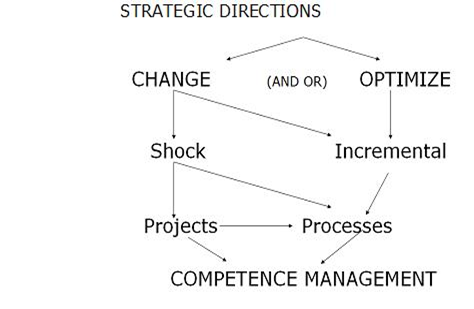
Fig.
3 The Strategy Execution Process As
the illustration suggests, there are two major directions to take when
executing a strategic plan: changing the rules of the game or the
organisational behaviour in case the results are disappointing or optimize the
existing, successful strategy. The “how”
to this “what” can be both shock therapy or an incremental “frog in the pot of
tepid water” approach. ultimately it will lead to managing the organisational
competences, be they individual or group competences. The “where” is in
projects or in processes, i.e. in new ventures or in routine things people do
in the organisation. The “why” is not in this picture as it is supported by the
collaborative strategy process manager as described above.
Conclusion
Strategy
management is a slightly more complex phenomenon than the cybernetic view some
scholars and managers have. An organization is a living thing, the environment
is something even the biggest organisations can’t control (unless they are in a
socialist island republic). Therefore, adaptive strategy management is the way
forward.
Strategy
management 2.0. will be adaptive or it will become obsolete in a flattened
society, where successful organisations in the new economy have exchanged the
hierarchical, top down, cybernetic management paradigm for a customer centric,
responsive and adaptive organisation where people are motivated, empowered and
share a clear vision, a sense of purpose and understand the general direction the organisation is heading. Only
that way, these organisations can face the challenges of a mobile, fragmented
and volatile generation Z and build a sustainable business.
[i] I use the
definition from Tom Gruber from Stanford University: “In
the context of knowledge sharing, I use the term ontology to mean a specification
of a conceptualization. That is, an ontology is a description (like a
formal specification of a program) of the concepts and relationships that can
exist for an agent or a community of agents. This definition is consistent with
the usage of ontology as set-of-concept-definitions, but more general. And it
is certainly a different sense of the word than its use in philosophy.” From:
T. R. Gruber. “A translation approach to portable ontologies.” Knowledge
Acquisition, 5(2):199-220, 1993
[i] In many
cases, this cause-effect identification process is a matter of preparing the
strategy formulation phase which has the implicit message: “This is how we see
things” or a misused word in the business jargon: the often overstated “paradigms”.
[ii] From: Mintzberg, Henry: “The Rise and Fall of Strategic Planning”
pp. 24-27, The Free Press 1994.
|